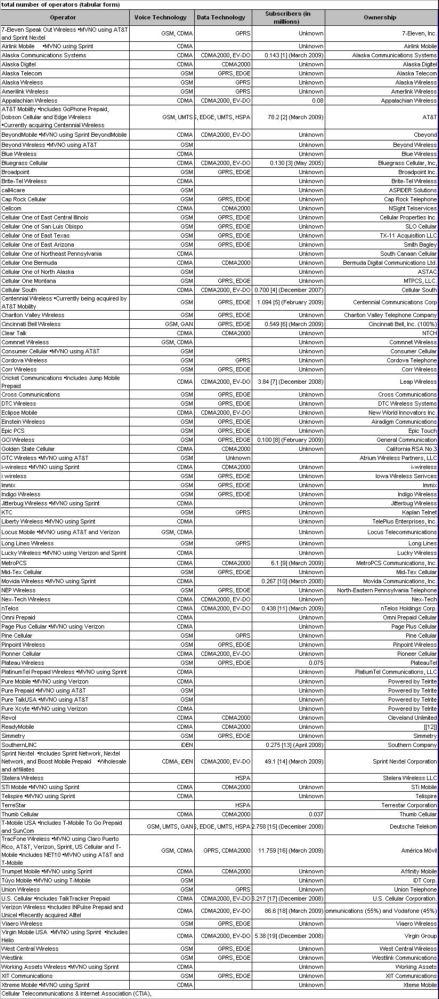
Out of the total 180 facilities-based wireless providers (as per the CTIA report) of the country, Verizon, AT&T, Sprint Nextel Corporation and T-Mobile USA are the four dominant wireless players.
In US, there are a total of two prime digital technologies and two less-widely used technologies, which are together referred to as Second Generation, or 2G. Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) and Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) are the two chief technologies, while integrated Digital Enhanced Network (iDEN) and Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) are less widely used.
Verizon Wireless offers its services over the CDMA platform. The operator has deployed EV-DO and EV-DO Rev, which offers a download speed range of 400 to 700 kbps with an upload speed that ranges from 50-70 kbps. Earlier last year, Verizon Wireless has further expanded its EV-DO Rev in areas of the country covering approximately 210 million people and had upgraded this entire EV-DO network footprint with EV-DO Rev. Henceforth, Verizon has continued to extend the reach of its EV-DO Rev, making it reach over 240 million people by the end of 2007.
Verizon Wireless also has announced that it plans to deploy LTE as its Fourth Generation, or “4G,” network technology. LTE is believed to offer faster data rates, and lower latency.
AT&T which happens to be a fierce competitor of Verizon, uses GSM/TDMA as its 2G digital technology and in the past year it has undertaken some up gradation of its mobile broadband network. It expanded its WCDMA/HSDPA network to more than 16 markets, including most of the top 100 cities in the United States, and planned to continue deploying WCDMA/HSDPA technology throughout a majority of the U.S. markets covered by its legacy network footprint. Since then, AT&T has further expanded its WCDMA/HSDPA network to more than markets, started the first U.S. deployment of HSUPA technology and upgraded its entire WCDMA/HSDPA network footprint with HSUPA technology.
Sprint Nextel Corp. uses CDMA platform for offering its mobile services. IT uses iDEN technology on the former Nextel network.
In the past year, the operator has expanded its EV-DO Rev and has upgraded over 82 percent of its CDMA network to EV-DO Rev. In addition to offering Sprint Nextel-branded wireless services over its CDMA network, Sprint Nextel continues to provide Nextel-branded and Boost Mobile prepaid wireless services over the former Nextel iDEN network, which operates in 355 metropolitan markets covering about 266 million people.
In a move to offer customers the benefits of both of its networks, and to relieve capacity constraints on its iDEN network, Sprint Nextel continues to offer a line of dual-mode handsets, marketed as PowerSource, that operate on both the CDMA and iDEN platforms. Plans of launching QChat devices lay underway.
T-Mobile is a GSM-based operator and has a countrywide EDGE network and said it will deploy a 3G next generation network. Starting with May, 2008, the operator made its first commercial step in the rollout of its 3G wireless network by launching its WCDMA/HSDPA network in New York City and later followed it with its deployment across 13 major metropolitan markets, such as New York, Boston, Miami, Las Vegas, and Houston.
Furthermore, T-Mobile said it expects to expand the network to 27 major markets, making T-Mobile 3G services available to more than two-thirds of the company’s current data customers.
|